
This Massive Open Online Course (MOOC) looks at the security issues connected with social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn or Google+. This MOOC builds on content from the Information Security modules that is part of the BSc (Hons) Business Information Technology programme. This MOOC covers topics including…
- Controlling privacy settings
- Choosing and managing passwords
- Physical security precautions
- Location settings and social media
Improve your understanding of social media security and avoid becoming a victim of hackers and scammers.
Privacy settings on social media
Privacy settings on social media
Privacy settings should be used to protect yourself when you are using social media websites.
Privacy settings and social networking
About 75% of students use Twitter constantly throughout the day – are you an active social media users? Have you looks at the privacy settings on your social media accounts? Did you know that about 10% of young people fail to secure a job because of the public content they have on their Facebook profile? The following series of videos explain how you can control your privacy settings on Facebook and Twitter.
Who can see me on Facebook?
Who can see your stuff on Facebook – MOOC
Who can look you up on Facebook?
Who can look you up on Facebook? – MOOC
Who can contact you on Facebook?
Who can contact you on Facebook? – MOOC
Twitter privacy settings
How to change privacy settings on Twitter – MOOC
Activity 1 – Privacy settings
- Make sure you are not signed in to Facebook
- Go to a popular search engine such as www.google.co.uk
- Type in the profile name you are currently using for Facebook
- Click on your profile
- View the content on your profile that is visible to others. Can you see any phone numbers, posts, pictures or videos?
- Is there too much content visible? Write down what content you would prefer to be private
- Now login to Facebook
- Go to the privacy section and change your privacy settings
Passwords and online profiles
A password is used to block other people from accessing your information. The best password is something others cannot guess or easily break using ‘cracking’ software. Despite knowing this we all tend to use special dates, pets names or even a city for even the most important passwords. Passwords with a mixture of characters, numbers and punctuation marks are stronger making them harder to guess or break.
It is all too easy and convenient to set one password for all your online profiles but this makes it too easy for others to access all of your profiles (which are probably connected via links). If you have more than 5 different passwords chances are you will eventually forget one of them. Your social media profiles are secure but you still need to remember the password for each site.
You could create a word document and use a system to hide the passwords within a large essay or document – for example the first character of each line could be a character in the password. This will allow you to access your password without anyone else guessing it. Name the document in a way that does not hint that it is hiding your passwords. You could also consider keychain software that securely stores multiple passwords – obviously protected with a password.
Is your password secure? Interview with Dr Andrew Schofield – MOOC
Activity 2: Generate strong passwords
- Create a new password with a password generator. Change the options to produce new passwords.
- Use a password strength indicator to show the strength of your new passwords. Compare this strength with your existing passwords.
Activity 3: Password selections
Consider the following passwords. Write down which you think are the strongest.
| Abc123 | A1b2c3d4 |
| R4c7x3E1f | R4c7x3e1f |
| Password | P@55WORD |
| Go!jets#1!! | Admin |
| M^s1ster|$ alw4ysf1ne! | Sister |
| Manchester | MaNcHeStErM16 |
Now create a password using the elements from the following list. Consider the previous advice to create the password.
| Dad | See | Cat | £ | : | Home | Helps | 5 | 8 | 3 |
| 1 | 0 | Mum | Sister | Brother | Happy | House | Sad | Wet | Hot |
| Boy | Girl | Day | Night | Today | Next | Love | Water | Ball | Pray |
| 2 | 4 | 6 | 7 | Swim | Big | You | 9 | See | 10 |
| Dog | * | Yellow | Month | Year | March | Phone | Manchester | Uk | London |
Physical security
Physical security is all about the unauthorised access of personal property and its protection from damage and harm. There are many risks. For example, leaving a personal device lying around, clicking on unknown links 0r opening emails that appears to be from a friend.
Leaving computer unattended
Do you recognise this situation? By walking away from your computer while it’s still on or leaving your social networking sites logged in you are making your personal information vulnerable. Always log out. Then close the browser window. But even closing the web browser window doesn’t guarantee you have logged out. Once you have finished working on any computer anywhere, it’s important that you log out and shut the computer down. Never use pubic WiFi for accessing sensitive information such as online banking or logging into social media profiles.
Don’t leave valuables lying around
Leaving mobile phones lying around or letting friends and family borrow them isn’t always a good idea. This simple action could be the beginning of many problems. For example, if you don’t lock your messages and log out of all your social media sites you are asking for “social media fun”. 
Anyone with access to your phone can access your social networks and do something apparently in your name “for fun” or worse.
Sharing passwords
Passwords are valuable information and should not be shared.
Passwords should be changed regularly. When creating a password for social networking sites don’t ask friends for advice or set their names as the password.
Writing passwords and user names
The graph below shows some of the main methods of remembering passwords in Sweden (series 1 – blue), UK (series 2 – orange) and Germany (series 3 – grey). 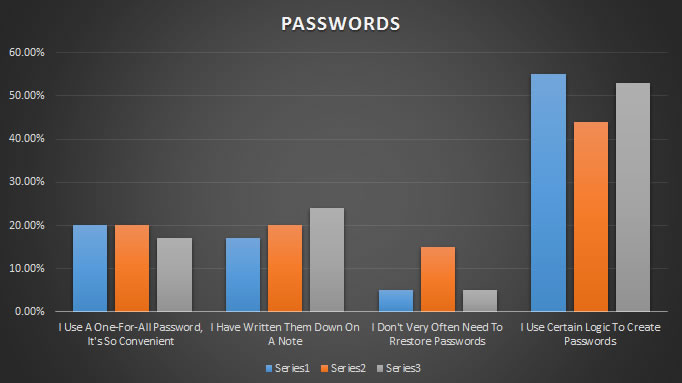
The research shows that there are still some people who use same password, write them down or don’t have a method for remembering them. Even when you have created a strong password it should be changed regularly.
The longer a password is left unchanged the greater the window of opportunity for a hacker to successful identify your password. Some systems force you to make regular password changes but even if a system does not require you to change a password this is not an indicator of its strength and you should still change your password regularly. Strong passwords can be difficult to remember.
Sharing too much information
Don’t display too much personal information about yourself online where it can be accessed by strangers. For example, be cautious about adding all your personal information on social networking sites. While it may look like all of these details are ‘required’ in most cases only the minimum level of information is required for registration before you can access a social network site. It is important that you set security and privacy settings to only allow friends, contacts or followers to see more of your information.
Downloading apps
Installing apps onto your phone is also a potential security threat. Apps may collect information about you and then unknowingly share it with third parties. In many cases you have given your permission to do this when the app was first installed. It is important to read what other people are saying about the app and to read the End User License Agreement (EULA) before installing anything.
False alerts on Facebook and other social media platforms
Malicious links to false videos and photos are regularly posted on Facebook and other social media platforms. They could be presented as news, events or celebrity gossip. These links can lead you to phishing sites or can start an automatic malware download on your computer once clicked.
Baiting
Baiting happens when someone gives you a USB drive or other electronic media that is preloaded with malware in the hope you will use the device and enable them to hack your computer. Do not use any electronic storage device, unless you know its origin is legitimate and safe. Scan all electronic media for viruses before use and make sure you keep your anti-virus software up-to-date.
Click-jacking
This is the concealment of hyperlinks beneath legitimate clickable content. For example, the link text or image might describe a legitimate link destination, but the actual hyperlink takes you somewhere else. When clicked, this causes a user to unknowingly perform actions, such as downloading malware or sending your ID to a site. Numerous click-jacking scams have employed the “Like” or “Share” buttons on social networking sites. Disable scripting and iframes in the browser you use. Consider further ways to set your browser options to maximize security.
Video tutorials
Physical breach
Information security responsibilities of employees
Password policy
Password policy – information security
Activity 4 – Test your knowledge
Location settings and social media
Information about the physical location of an individual can be captured and stored from social media activity. A Global Positioning Systems (GPS) receiver is found in most mobile phones. The phone can share your current location onto social media sites. Several social media networks are entirely reliant on your location information. For example, Foursquare shows your location on a map and offers a chance to meet new friends. However, you should be careful when enabling this type of information on your social media check ins. Burglars might be monitoring your checkins and planning to checkin into your home!  Social Media Infographic Provided by CreditSesame.com
Social Media Infographic Provided by CreditSesame.com
Location settings and security
You can also use technology to fight back. There are location tracking security apps that can be used to locate a lost or stolen mobile device.
Find my iPhone
Find my iPhone is a popular security app for iOS devices that uses the phone’s GPS receiver. Users can remotely locate or wipe their iOS devices using real time location tracking. The app’s lost mode allows the remote setting of a pass code that locks the device. The second mode can erase the contents of the iPhone from any location.
How to use Find my iPhone
The next video demonstrates how to download and install Find my iPhone. It also briefly explains Find my iPhone its benefits.
Activity 5: Find my iPhone
- Open the app store
- Login to the app store
- Search for “Find my iPhone”
- From the search results click on “Find my iPhone”
- Download “Find my iPhone”
- Follow the instructions to set it up the app
This image shows how Find my iPhone can locate a lost or stolen iPhone using GPS tracking. 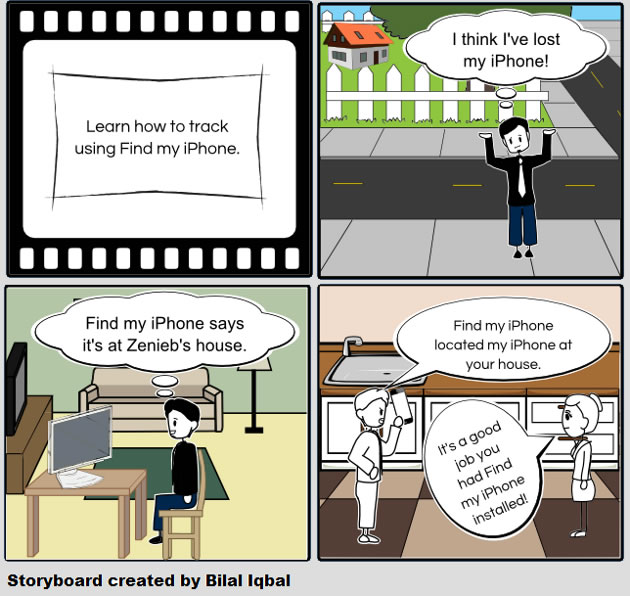
Activity 6: Test your Find my iPhone installation
- Enable WiFi or 3G on you iPhone
- Using any web browser login to iCloud on your computer
- Click on “Find my iPhone”
- You have now tracked you iPhone using GPS tracking
Do you know anyone who could benefit from learning more about social media security? Please do share this post!
This post was prepared for you by Business Information Technology students; Mohammed Anjum, Rimiz Hussain, Bilal Iqbal and Zeniab Khurshid


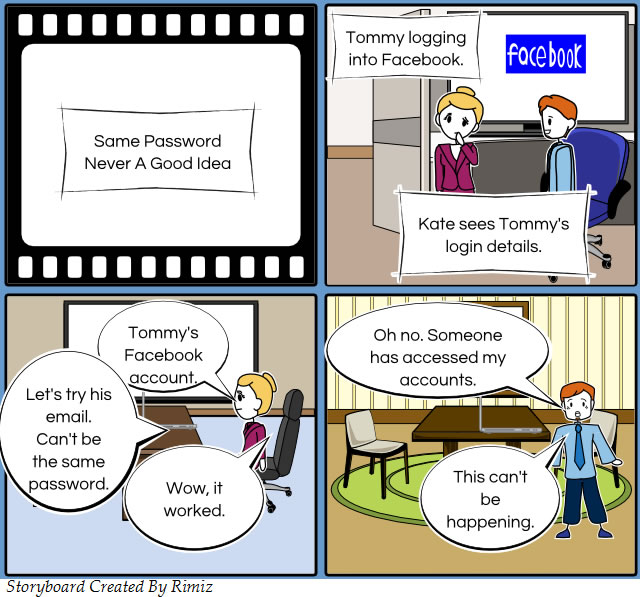

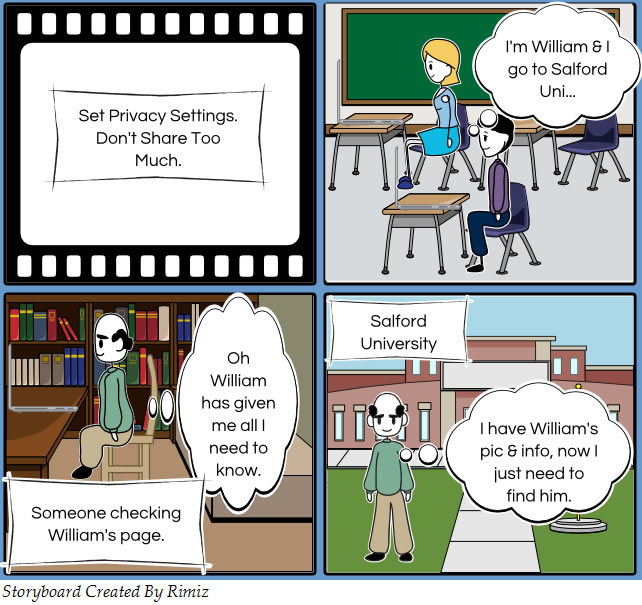
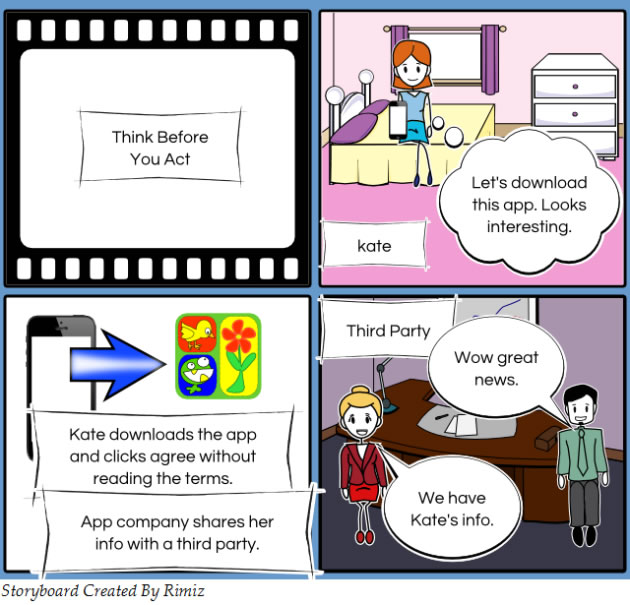
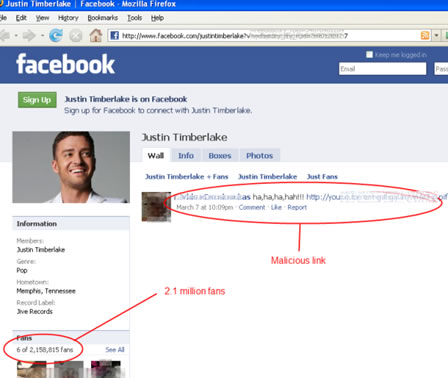
Love the storyboards – they were created at http://www.storyboardthat.com
I have some question
What do people think would be a good blog hosting website for creating a blog on? There are a lot I think so I don’t know which would be most useful and versatile..
Funny
How do I make my own Blogger layout? I already made a header, I want to learn how to make a matching layout?